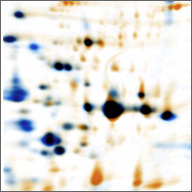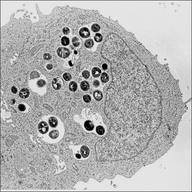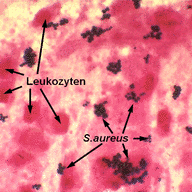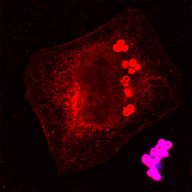
C4: Characterization of the immune proteome of Staphylococcus aureus
We wish to understand how the adaptive immune system protects against Staphylococcus aureus, often for a lifetime, why protection occasionally breaks down, and under which conditions the anti-bacterial immune response may be harmful. Considering the diversity and complexity of S. aureus and its human host, we use a personalized approach in order to elucidate the general rules governing the immune response to the bacteria
Knowledge of the microbial immunome, i.e., a panoramic view of the T- and B-cell responses against S. aureus, will be an important step toward the development of effective vaccines.
Contact
Prof. Dr. Barbara Bröker
Institut für Immunologie und Transfusionsmedizin
Ernst-Moritz-Arndt-Universität Greifswald
Sauerbruchstraße
D-17489 Greifswald
Phone +49 3834 865595
Fax +49 3834 865490
E-Mail: broeker@uni-greifswald.de
C6: Post-invasion events in Staphylococcus aureus-infected host cells – A combined transcriptomics/proteomics in vivo approach
In vivo OMICs approaches provide a comprehensive view of the host-pathogen interplay and the pathophysiology of S. aureus. We will record and interpret time-resolved combined proteomics and transcriptomics data of internalization models with professional and non-professional phagocytes in cell culture, a murine i.v. infection model and selected patient samples
In parallel, we will address whether bacterial subpopulations exist in infection, how they differ and how they might jointly accomplish adaptation to the host. In summary, the comprehensive monitoring of pathogen-host interplay will show us the progression of the infection process in unprecedented detail.
Contact
Prof. Dr. Jörg Vogel
Institut für Molekulare Infektionsbiologie
Julius-Maximilians-Universität Würzburg
Josef-Schneider-Str. 2
D-97080 Würzburg
Phone +49 931 3182575
Fax +49 931 3182578
E-Mail: joerg.vogel@uni-wuerzburg.de
Prof. Dr. Uwe Völker
Interfakultäres Institut für Genetik und Funktionelle Genomforschung
Abteilung für Funktionelle Genomforschung
Ernst-Moritz-Arndt-Universität Greifswald
Friedrich-Ludwig-Jahn-Str. 15A
D-17489 Greifswald
Phone +49 3834 865870
Fax +49 3834 8680012
E-Mail: voelker@uni-greifswald.de
C7: Staphylococcus aureus in the airways of cystic fibrosis patients, a human model for long-term adaptive interaction
To elucidate triggers involved in the adaptation process of S. aureus to the airways of CF patients during persistent infection on the transcription level, we plan to investigate transcription start sites, non-coding RNA and epigenetic base modifications using differential RNA and PacBio sequencing.
The functional impact of detected changes in persisting isolates on the host-pathogen interaction will be determined by infecting CF respiratory epithelial cells and mice with dedicated deletion mutants. Variation and fluctuation of the S. aureus population in persistently infected CF patients during a 1-year clinical study will be characterized on genomic, metabolomic, and proteomic levels.
Contact
PD Dr. Alexander Mellmann
Universitätsklinikum Münster
Robert-Koch-Str. 41
D-48149 Münster
Phone +49 251 8352316
Fax +49 251 8355688
E-Mail: mellmann@uni-muenster.de
Prof. Dr. Barbara C. Kahl
Universitätsklinikum Münster
Domagkstr. 10
D-48149 Münster
Phone +49 251 8355381
Fax +49 251 8355350
E-Mail: kahl@uni-muenster.de
C8: The impact of the host glyco-receptor repertoire on staphylococcal tissue specificity
The interaction of S. aureus with cells of the body linings is multifactorial and only partially understood. The cell wall teichoic acid (WTA) of S. aureus is an important modulator of S. aureus adhesion to different cell types.
Therefore, we propose to elucidate the molecular details and structure-function relationship of WTA-receptor binding of different scavenger receptors, which are expressed in a variety of host cells. We will use these data to understand the interaction of S. aureus with different host surfaces in vivo and correlate this with the ability of S. aureus to colonize the host and infect virtually every organ.
Contact
Dr. Christopher Weidenmaier
Interfakultäres Institut für Mikrobiologie und Infektionsmedizin
Eberhard-Karls-Universität Tübingen
Elfriede-Aulhorn-Straße 6
D-72076 Tübingen
Phone +49 7071 2981526
Fax +49 7071 295440
E-Mail: christopher.weidenmaier@med.uni-tuebingen.de
C10: Characterizing and deciphering the interaction of platelets and monocytes with Staphylococcus aureus
Staphylococcus aureus infections are associated with activation and aggregation of platelets as well as activation of monocytes. The goal of this study will be the identification of strong and weak platelet-activating staphylococcal proteins.
We will first screen S. aureus clinical strain for their ability to activate platelets and then use the enriched soluble surface-exposed and secreted proteins to analyze platelet and monocyte activation. The surface proteome and secretome of the selected staphylococci will be compared to explore potential candidates for S. aureus-platelet/monocyte interaction. With the purified S. aureus-derived proteins, we will characterize the induced signaling pathways in platelets and monocytes using phosphoproteomics.
Contact
Prof. Dr. Sven Hammerschmidt
Interfakultäres Institut für Genetik und Funktionelle Genomforschung
Abteilung Genetik der Mikroorganismen
Ernst-Moritz-Arndt-Universität Greifswald
Friedrich-Ludwig-Jahn-Straß 15a
D-17487 Greifswald
Phone +49 3834 864160
Fax +49 3834 864172
E-Mail: sven.hammerschmidt@uni-greifswald.de
Prof. Dr. Andreas Greinacher
Institut für Immunologie und Transfusionsmedizin, Abteilung für Transfusionsmedizin,
Universitätsmedizin Greifswald,
Sauerbruchstraße, Neubau P
D-17475 Greifswald
Phone: 03834-86 5482
E-mail: greinach@uni-greifswald.de
C11: Host cell death induced by Staphylococcus aureus and its linkage to phagosomal escape
We previously identified host signaling networks involved in S. aureus-induced host cell death as well as pathogen factors supporting phagosomal escape of S. aureus and host cell death. In this project, we aim to further investigate the identified host factors and pathways involved in infection-induced cell death.
Cellular cytotoxicity networks will be connected to bacterial factors, and their role in S. aureus-induced pathology will be investigated in animal models. We will examine the mode of action for selected identified bacterial virulence factors and identify those required for establishing infections in vivo by using targeted mutants and applying in vivo TnSeq screens.
Contact
Prof. Dr. Thomas Rudel
Lehrstuhl für Mikrobiologie, Biozentrum
Julius-Maximilians-Universitä?t Würzburg
Am Hubland
D-97074 Würzburg
Phone +49 931 3184401
Fax +49 931 8884402
E-Mail: thomas.rudel@biozentrum.uni-wuerzburg.de
Dr. Martin Fraunholz
Lehrstuhl für Mikrobiologie,
Biozentrum der Julius-Maximilians-Universität Würzburg
Am Hubland, 97074 Würzburg
Phone: +49 931 3183242
E-Mail: martin.fraunholz@uni-wuerzburg.de
C12: Detecting and deciphering Staphylococcus aureus strategies that cause chronic and persistent infections
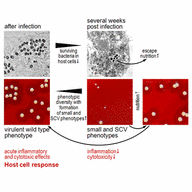
S. aureus is a very versatile human pathogen which causes different types of invasive infection that can take a chronic and therapy-refractory course. The pathogenic mechanisms include the bacterial ability to invade different types of professional (e.g., macrophages) and non-professional phagocytes (e.g., endothelial, epithelial cells and osteoblasts), escape from the host’s lysosomal degradation machinery and persist intracellularly while developing dormant small colony variant (SCV) phenotypes.
This project aims to decipher the bacterial regulatory mechanisms that underlie the dynamic phenotype-switching process between wild type and SCVs, which are possible targets for novel preventive and therapeutic strategies.
Contact
PD Dr. Bettina Löffler
Institut für Medizinische Mikrobiologie
Universitätsklinikum Münster
Domagkstr. 10
48149 Münster
Tel. +49 251 8355378
Fax +49 251 8355350
E-Mail: loeffleb@uni-muenster.de
Prof. Dr. Georg Peters
Institut für Medizinische Mikrobiologie
Universitätsklinikum Münster
Domagkstr. 10
D-48149 Münster
Phone +49 251 8355340
Fax +49 251 8355350
E-Mail: georg.peters@uni-muenster.de
C13: Molecular interactions of Staphylococcus aureus with professional phagocytes
This project aims to characterize the molecular response mechanism of different subpopulations of macrophages (M1 vs M2) to infections with Staphylococcus aureus. Using well-characterized strains of S. aureus, including small colony variants (SCVs), we will analyze which subpopulations of murine macrophages are important for effective control of infection or may, on the contrary, serve as a reservoir of S. aureus.
Using cell culture and appropriate mouse knock-out models, we intend to reveal the survival strategies of S. aureus in professional phagocytes and identify novel molecular targets for modulation of S. aureus-induced inflammation.
Contact
Dr. Katarzyna Barczyk-Kahlert
Institut für Immunologie,
Universitätsklinikum Münster
Röntgenstr. 21
D-48149 Münster
Phone: +49 251-8352945
E-mail: bar@uni-muenster.de
Prof. Dr. Johannes Roth
Institut für Immunologie
Universitätsklinikum Münster
Röntgenstr. 21
D-48149 Münster
Phone +49 251 8356578
Fax +49 251 8356549
E-Mail: rothj@uni-muenster.de
C14: In vivo investigation of the role of adhesins in Staphylococcus aureus-induced infective endocarditis and development of a diagnostic imaging marker
Infective endocarditis (IE) caused by Staphylococcus aureus is mediated by a complex interplay of different adhesive molecules (adhesins). This project aims to elucidate the role of individual adhesins and their interactions.
We will use non-invasive magnetic resonance imaging for longitudinal assessment of an in vivo mouse model, in which endocarditis is induced by different isogenic S. aureus mutants with knockout of individual adhesins. Based on the findings about essential adhesins, the second aim of this project is the development of a non-invasive imaging marker to specifically detect S. aureus-induced IE.
Contact
Prof. Dr. Cornelius Faber
Institut für Klinische Radiologie
Universitätsklinikum Münster
Westfälische Wilhelms-Universität Münster
Waldeyerstr. 1
D-48149 Münster
Phone +49 251 8357608
Fax +49 251 8352067
E-Mail: faberc@uni-muenster.de
Dr. Verena Hörr
Institut für Klinische Radiologie
Universitätsklinikum Münster
Albert-Schweitzer-Campus 1, Gebäude A16
D-48149 Münster
Phone: +49 251 8352418
E-Mail: vhoerr@uni-muenster.de
PD Dr. Bettina Löffler
Institut für Medizinische Mikrobiologie
Universitätsklinikum Münster
Domagkstr. 10
D-48149 Münster
Phone +49 251 8355378
Fax +49 251 8355350
E-Mail: loeffleb@uni-muenster.de
C15: Differential activation of formyl peptide receptors by Staphylococcus aureus and consequences for inflammation
Formyl peptide receptors (FPR1-3) are important pattern recognition receptors governing leukocyte chemotaxis and cytokine release. We have recently demonstrated that phenol-soluble modulin (PSM) peptides from highly pathogenic Staphylococcus aureus are not only important cytolytic toxins but also highly effective ligands for FPR2.
FPR1 and FPR2 appear to be strongly synergetic, while the amounts of FPR1 and FPR2 ligands vary greatly between staphylococcal strains. This project aims at unraveling these crucial aspects of innate immunity against S. aureus to understand how the variable S. aureus factors may affect leukocyte responses.
Contact
Dr. Dorothee M. Kretschmer
Interfakultäres Institut für Mikrobiologie und Infektionsmedizin,
Eberhard-Karls-Universität Tübingen
Elfriede-Aulhorn-Str.6
D-72076 Tübingen
Phone: +49 7071-2981514
E-Mail: dorothee.kretschmer@med.uni-tuebingen.de
C16: Host-pathogen interaction of Staphylococcus aureus – insight from a population-based perspective
This project will focus on the host factors influencing the human adaptive immune response to Staphylococcus aureus. We propose that besides differential bacterial exposure, a combination of human genetic determinants and molecular composition of body fluids is decisive.
In our analysis, we will take a population-based approach. Analyzing samples from the subjects of the Study of Health in Pomerania (SHIP), we will profile the proteomes of colonizing S. aureus strains and the specific serum antibodies. These data will be examined for correlation with existing multi OMICs SHIP data to reveal host factors that i) distinguish between high and low immune responders to S. aureus, and ii) determine the risk of developing allergic reactions to S. aureus.
Contact
Prof. Dr. Barbara Bröker
Institut für Immunologie und Transfusionsmedizin
Ernst-Moritz-Arndt-Universität Greifswald
Sauerbruchstraße, DZ 7
D-17489 Greifswald
Phone +49 3834 865595
Fax +49 3834 865490
E-Mail: broeker@uni-greifswald.de
Prof. Dr. Uwe Völker
Interfakultäres Institut für Genetik und Funktionelle Genomforschung
Abteilung für Funktionelle Genomforschung
Ernst-Moritz-Arndt-Universität Greifswald
Friedrich-Ludwig-Jahn-Str. 15A
D-17489 Greifswald
Phone +49 3834 865870
Fax +49 3834 8680012
E-Mail: voelker@uni-greifswald.de
| |||||